Array
An array is a collection of items stored at contiguous memory locations. The idea is to store multiple items of the same type together. This makes it easier to calculate the position of each element by simply adding an offset to a base value, i.e., the memory location of the first element of the array (generally denoted by the name of the array).
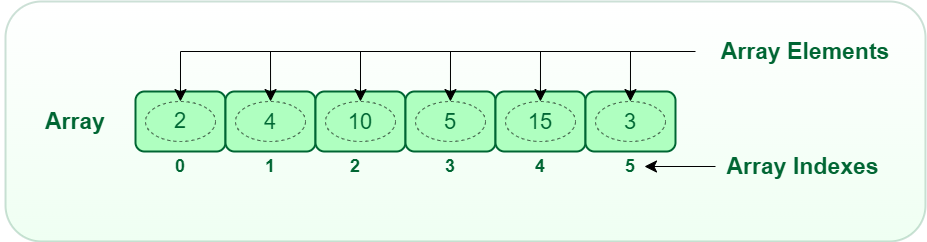
In kotlin we can create array as following:
Using Array class
fun main() {
// Creates an Array<String> with values ["0", "1", "4", "9", "16"]
val asc = Array(5) { i -> (i * i).toString() }
asc.forEach { println(it) }
}
Using arrayOf()
fun main() {
// Creates an Array<Int> with values ["0", "1", "4", "9", "16"]
val asc = arrayOf(0,1,2,3,4,5)
asc.forEach { println(it) }
}
Using Primitive Types
Kotlin also has classes that represent arrays of primitive types without boxing overhead: ByteArray, ShortArray, IntArray, and so on. These classes have no inheritance relation to the Array class, but they have the same set of methods and properties. Each of them also has a corresponding factory function:
fun main() {
val x: IntArray = intArrayOf(1, 2, 3)
x[0] = x[1] + x[2]
x.forEach { println(it) }
}
references:
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/array-data-structure/
https://kotlinlang.org/docs/arrays.html#primitive-type-arrays