Linked List
A linked list is a linear data structure, in which the elements are not stored at contiguous memory locations. The elements in a linked list are linked using pointers as shown in the below image:
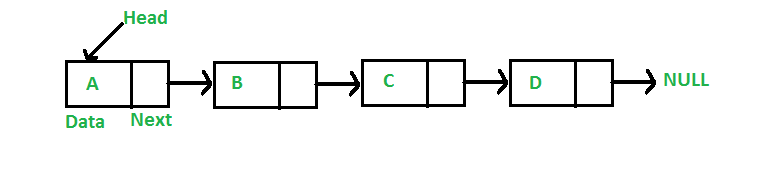
In simple words, a linked list consists of nodes where each node contains a data field and a reference(link) to the next node in the list.
Types
We have some different types of linked list with some specific differents bettween them, that are:
Singly Linked List
Structure:
/**
* Node for each element of linked list.
*
* @param element is the value inserted on this Node.
* @see T is the type expected , can be an object or just a primitive type as Int.
*/
class Node<T>(private val element: T) {
var value = element
var next: Node<T>? = null
}
class SinglyLinkedList<T> {
private var head: Node<T>? = null
fun addNode(element: T) {
val newNode = Node(element)
if (head == null) {
head = newNode
} else {
var current = head
while (current?.next != null) {
current = current.next
}
current?.next = newNode
}
}
fun forEach(action: (T) -> Unit) {
var current = head
while (current?.next != null) {
action(current.value)
current = current.next
}
}
}
fun main() {
val singlyLinkedList: SinglyLinkedList<Int> = SinglyLinkedList()
for (i in 1..6) {
singlyLinkedList.addNode(i)
}
singlyLinkedList.forEach { value ->
println(value)
}
}For what it's
It is used to implement stacks and queues which are like fundamental needs throughout computer science. To prevent the collision between the data in the hash map, we use a singly linked list.Doubly Linked List
A doubly linked list of singly linked lists is a data structure that consists of a set of singly linked lists (SLLs), each of which is doubly linked. It is used to store data in a way that allows for fast insertion and deletion of elements. Each SLL is made up of two parts: a head and a tail. The head of each SLL contains a pointer to the first element in the list, and the tail contains a pointer to the last element. It is advantageous over other data structures because it allows for quick insertion and deletion of elements. Additionally, it is easy to implement and can be used in a variety of applications.
Structure:
/**
* Node to represent each space allocated for each element inserted on list.
*/
private class Node<T>(element: T) {
val value = element
var prev: Node<T>? = null
var next: Node<T>? = null
}
class DoublyLinkedList<T> {
private var head: Node<T>? = null
private var tail: Node<T>? = null
/**
* 1 head = 1, tail = 1
* 2 head = 1 , tail = 2
* 3 head = 1, tail = 3
*/
fun addElement(value: T) {
val newElement = Node(value)
if (head == null) {
head = newElement
tail = newElement
} else {
var current = head
while (current?.next != null) {
current = current.next
}
tail = newElement
newElement.prev = current
current?.next = newElement
}
}
fun forEach(reverse: Boolean = false, action: (T) -> Unit) {
if (reverse) {
var current = tail
while (current?.prev != null) {
action(current.value)
current = current.prev
}
current?.value?.let { action(it) }
} else {
var current = head
while (current?.next != null) {
action(current.value)
current = current.next
}
}
}
}
fun main() {
val doublyLinkedList: DoublyLinkedList<Int> = DoublyLinkedList()
for (i in 1..6) {
doublyLinkedList.addElement(i)
}
doublyLinkedList.forEach { value ->
print("$value,")
}
println()
doublyLinkedList.forEach(true) { value ->
print("$value,")
}
}For what it's
Implementing a music or video playlist: a doubly linked list allows easy traversal of a playlist both forwards and backwards. Each song or video can be represented by a node in the list, with each node having a forward and backward pointer to allow easy navigation. Browser history: A browser history can be implemented using a doubly linked list, where each web page is represented by a node in the list, with each node having a forward and backward pointer. This allows users to navigate their browsing history both forwards and backwards. Text editors: Doubly linked lists can be used to implement text editors, where each line of text is represented by a node in the list. Each node has a forward and backward pointer to allow easy navigation between lines of text.Circular Linked List
Imagine you are working on a project to create a music playlist application. Each song in the playlist is represented by a node in a doubly linked list. The doubly linked list allows the user to easily traverse the playlist both forwards and backwards. Furthermore, the user can easily add or remove a song from the playlist by inserting or deleting a node in the list. This is because each node has two links that can be updated to point to the new node or bypass a deleted node
Structure
/**
* Class to represent each node on circular linked list.
*/
private class Node<T>(element: T) {
val value = element
var next: Node<T>? = null
}
private class SinglyCircularLinkedList<T> {
var head: Node<T>? = null
fun addItem(element: T) {
val newElement = Node(element)
if (head == null) {
head = newElement
newElement.next = head
} else {
var current = head
while (current?.next != head) {
current = current?.next
}
newElement.next = head
current?.next = newElement
}
}
fun traverse(until: Int? = null, action: (T) -> Unit) {
var current = head
if (until == null) {
while (true) {
if (current?.next == head) {
current?.value?.let { action(it) }
current?.next?.value?.let { action(it) }
break
} else {
current?.value?.let { action(it) }
}
current = current?.next
}
} else {
var i = 0
while (i < until) {
current?.value?.let { action(it) }
current = current?.next
i++
}
}
}
}
fun main() {
val singlyCircularLinkedList: SinglyCircularLinkedList<Int> = SinglyCircularLinkedList()
for (i in 1..6) {
singlyCircularLinkedList.addItem(i)
}
singlyCircularLinkedList.traverse { value ->
print("$value,")
}
println()
singlyCircularLinkedList.traverse(12) { value ->
print("$value,")
}
}For what it's
Managing tasks in a round-robin scheduling algorithm: In a round-robin scheduling algorithm, tasks are scheduled in a circular manner. Singly circular linked lists can be used to represent a queue of tasks, where each task is represented by a node in the list. The head of the list points to the first task, and the last node points back to the head, creating a circular list. This allows for efficient management of tasks in a round-robin scheduling algorithm. Traffic signal control: In a busy intersection, a traffic signal control system can be implemented using a singly circular linked list. Each traffic light can be represented as a node in the list, and the last traffic light in the list can be connected to the first traffic light, creating a loop. This allows the traffic signal control system to cycle through the traffic lights in a circular manner, ensuring that each direction of traffic gets its turn to proceed.Circular doubly linked list
A circular doubly linked list is a mixture of a doubly linked list and a circular linked list. Like the doubly linked list, it has an extra pointer called the previous pointer, and similar to the circular linked list, its last node points at the head node. This type of linked list is the bi-directional list. So, you can traverse it in both directions.Imagine you are working on a project to create a messaging application. Each message in the conversation is represented by a node in a double circular linked list. The double circular linked list allows the user to easily traverse the messages both forwards and backwards, as well as loop around to the beginning of the conversation once they reach the end.
Structure
private class Node<T>(element: T) {
val value = element
var next: Node<T>? = null
var prev: Node<T>? = null
}
private class DoublyCircularLinkedList<T> {
var head: Node<T>? = null
var tail: Node<T>? = null
fun addElement(element: T) {
val newElement = Node(element)
if (head == null) {
head = newElement
tail = newElement
tail?.next = head
tail?.prev = head
} else {
var current = head
head?.prev = tail
while (current?.next != head) {
current = current?.next
}
newElement.prev = current
newElement.next = head
tail = newElement
current?.next = newElement
}
}
fun traverse(until: Int? = null, action: (T) -> Unit) {
var current = head
if (until == null) {
while (true) {
if (current?.next == head) {
current?.value?.let(action)
current?.next?.value?.let(action)
break
} else {
current?.value?.let(action)
}
current = current?.next
}
} else {
var i = 0
while (i < until) {
current?.value?.let {
action(it)
}
current = current?.next
i++
}
}
}
fun reverse(until: Int? = null, action: (T) -> Unit) {
var current = tail
if (until == null) {
while (true) {
if (current?.prev == head) {
current?.value?.let(action)
current?.prev?.value?.let(action)
break
} else {
current?.value?.let(action)
}
current = current?.prev
}
} else {
var i = 0
while (i < until) {
current?.value?.let {
action(it)
}
current = current?.prev
i++
}
}
}
}
fun main() {
val doublyCircularLinkedList: DoublyCircularLinkedList<Int> = DoublyCircularLinkedList()
for (i in 1..6) {
doublyCircularLinkedList.addElement(i)
}
doublyCircularLinkedList.traverse { value ->
print("$value,")
}
println()
doublyCircularLinkedList.traverse(11) { value ->
print("$value,")
}
println()
doublyCircularLinkedList.reverse { value ->
print("$value,")
}
println()
doublyCircularLinkedList.reverse(11) { value ->
print("$value,")
}
}For what it's
Multiplayer games use a circular list to swap between players in a loop. One practical application of a doubly circular linked list is in implementing a playlist where users can navigate through the list of songs in both forward and backward directions. In this case, each song can be represented as a node in the list, and each node contains pointers to the next and previous songs in the list. The last song in the list is connected to the first song, creating a loop. Music playlists: A music playlist can be implemented using a doubly circular linked list. Each song can be represented as a node in the list, and each node contains pointers to the next and previous songs in the list. The last song in the list is connected to the first song, creating a loop. This allows the playlist to be played in both forward and backward directions, where the user can navigate to the next or previous song as desired. Image gallery: An image gallery can be implemented using a doubly circular linked list. Each image can be represented as a node in the list, and each node contains pointers to the next and previous images in the list. The last image in the list is connected to the first image, creating a loopREFERENCES:
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/data-structures/linked-list/ https://www.simplilearn.com/tutorials/data-structure-tutorial/types-of-linked-list https://www.scaler.com/topics/round-robin-scheduling-in-os/ https://iq.opengenus.org/applications-of-linked-list/ https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/java-util-hashmap-in-java-with-examples/